
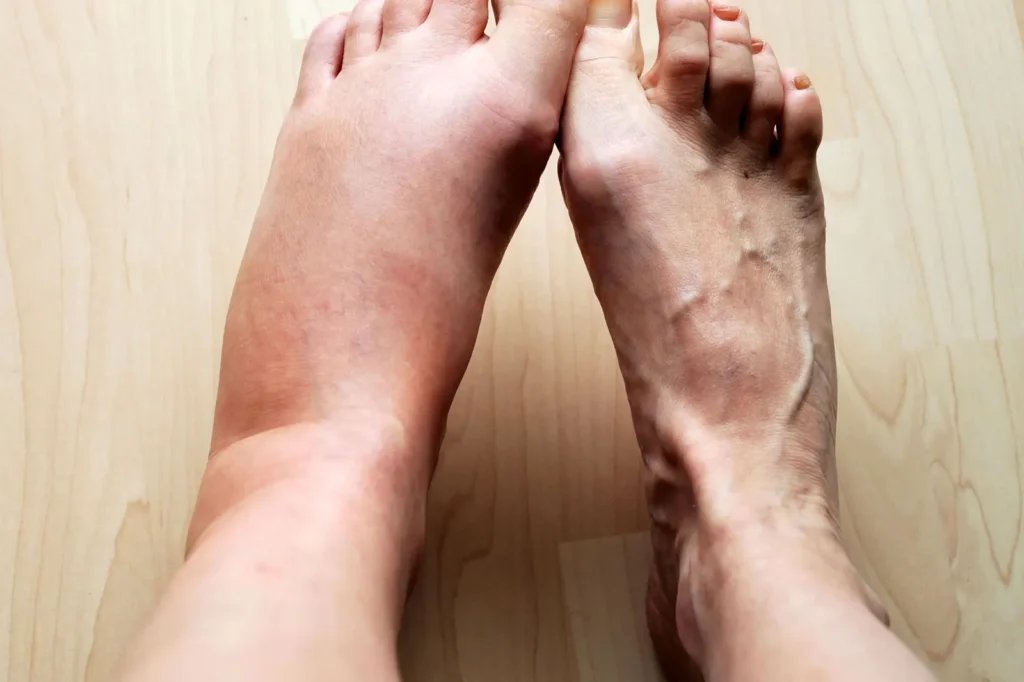
What is Inflammation

Inflammation is a natural and essential response of the body’s immune system to injury, infection, or harmful stimuli. It is a complex biological process that involves the activation of immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. While inflammation serves as a protective mechanism that aids in healing and recovery, it can become problematic when it persists over time or occurs inappropriately, leading to chronic inflammation.
Types of Inflammation
- Acute Inflammation:
Acute inflammation is a short-term response that occurs immediately after an injury or infection. Symptoms include redness, heat, swelling, pain, and loss of function in the affected area. This type of inflammation is beneficial, as it helps the body fight off pathogens and initiate the healing process. Examples include inflammation caused by a cut, sprain, or infection. - Chronic Inflammation:
Unlike acute inflammation, chronic inflammation lasts for an extended period, often weeks, months, or even years. It can result from unresolved acute inflammation, autoimmune disorders, persistent infections, or prolonged exposure to irritants. Chronic inflammation is linked to various health issues, including obesity, heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Symptoms may be less obvious and can include fatigue, body aches, and digestive issues.
The Inflammatory Response
When the body encounters harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, toxins, or damaged cells, the inflammatory response is triggered. Key components of this response include:
- Immune Cells: White blood cells, such as neutrophils and macrophages, are recruited to the site of injury or infection to eliminate pathogens and clear debris.
- Cytokines: These are signaling molecules that help regulate the immune response and promote inflammation. Pro-inflammatory cytokines can exacerbate inflammation, while anti-inflammatory cytokines help resolve it.
- Vasodilation: Blood vessels widen to increase blood flow to the affected area, allowing more immune cells to reach the site of injury. This process also contributes to the redness and heat associated with inflammation.
Causes of Inflammation
Inflammation can be triggered by various factors, including:
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, and fungal infections can provoke an inflammatory response.
- Injury: Physical injuries, such as cuts or fractures, can lead to localized inflammation.
- Chronic Stress: Long-term stress can contribute to persistent inflammation.
- Obesity: Excess fat tissue, particularly visceral fat, can produce pro-inflammatory substances, leading to chronic inflammation.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to pollutants, chemicals, and allergens can trigger inflammation.
How Chronic Inflammation Develops

Chronic inflammation is a prolonged and persistent inflammatory response that can have significant implications for overall health. Unlike acute inflammation, which is a short-term response to injury or infection, chronic inflammation can last for months or even years. Understanding how chronic inflammation develops is crucial for managing its effects on the body and preventing related health issues.
Key Factors Contributing to Chronic Inflammation
- Persistent Infections:
- Some infections, especially those caused by certain bacteria, viruses, or parasites, can lead to chronic inflammation if not fully resolved. The immune system remains activated as it attempts to fight off the lingering pathogens, resulting in a continuous inflammatory state.
- Autoimmune Disorders:
- In autoimmune diseases, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues as if they were foreign invaders. Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis can trigger chronic inflammation as the body’s immune response becomes misdirected, leading to ongoing inflammation and tissue damage.
- Chronic Stress:
- Prolonged psychological or physical stress can lead to increased levels of stress hormones, such as cortisol. While cortisol has anti-inflammatory properties, chronic stress can disrupt the balance, causing the immune system to remain in a heightened state of alert, contributing to persistent inflammation.
- Obesity:
- Excess body fat, particularly visceral fat (fat stored around the organs), is linked to chronic inflammation. Adipose tissue produces pro-inflammatory cytokines, which can promote an inflammatory response throughout the body. This is one reason why obesity is associated with a higher risk of various chronic diseases, including heart disease and diabetes.
- Environmental Factors:
- Exposure to environmental pollutants, toxins, and irritants can trigger inflammation. For instance, air pollution, heavy metals, and chemical exposure can lead to chronic inflammatory responses in the body. Lifestyle factors, such as smoking and poor diet, can further exacerbate inflammation.
- Dietary Choices:
- A diet high in refined sugars, unhealthy fats, and processed foods can promote inflammation. Certain food additives and preservatives may also contribute to inflammatory responses. Conversely, an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, healthy fats, and lean proteins can help mitigate chronic inflammation.
- Inactivity:
- A sedentary lifestyle can contribute to chronic inflammation. Regular physical activity has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects, while lack of movement can lead to weight gain and metabolic dysfunction, promoting inflammation.
Mechanisms of Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation involves complex biological processes, including:
- Cytokine Production: Pro-inflammatory cytokines are continuously released, perpetuating the inflammatory cycle. These signaling molecules can attract more immune cells to the site, leading to ongoing inflammation.
- Tissue Damage: Persistent inflammation can result in damage to surrounding tissues and organs, which can lead to further inflammatory responses as the body attempts to heal.
- Immune System Dysregulation: Chronic inflammation can alter the immune system’s normal functioning, leading to increased susceptibility to infections and diseases.
The Link Between Inflammation and Weight Loss
Inflammation plays a significant role in the body’s metabolic processes, and its relationship with weight loss is complex and multifaceted. While inflammation is a natural response to injury or infection, chronic inflammation can hinder weight loss efforts and contribute to various health issues. Understanding this connection is essential for those looking to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
How Inflammation Affects Metabolism
- Altered Metabolic Rate:
- Chronic inflammation can disrupt normal metabolic processes, leading to changes in how the body burns calories. Inflammatory markers can influence metabolic rate, potentially slowing it down and making it more difficult to lose weight. This is particularly relevant for individuals struggling with obesity, where inflammation is often present.
- Insulin Resistance:
- One of the key mechanisms linking inflammation and weight loss is insulin resistance. Chronic inflammation can impair the body’s ability to respond to insulin effectively, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Insulin resistance is associated with weight gain and can make it challenging to shed excess pounds. When the body’s insulin response is compromised, it can also lead to increased fat storage, particularly in the abdominal area.
- Hormonal Imbalance:
- Inflammation can affect the production and regulation of hormones that are crucial for weight management, such as leptin and ghrelin. Leptin, which signals satiety to the brain, may become less effective due to inflammation, leading to increased hunger and overeating. Conversely, elevated levels of ghrelin, the hunger hormone, can contribute to increased appetite and cravings, further complicating weight loss efforts.
Inflammation’s Impact on Appetite and Food Choices
- Changes in Appetite Regulation:
- Chronic inflammation can disrupt the signaling pathways involved in appetite regulation. Inflammatory cytokines can affect the hypothalamus—the part of the brain that controls hunger—leading to increased appetite and cravings for unhealthy, calorie-dense foods. This can create a vicious cycle, as consuming these foods may exacerbate inflammation.
- Food Cravings and Preferences:
- Individuals with chronic inflammation may find themselves craving comfort foods, often high in sugar and unhealthy fats. These foods can provide temporary relief and pleasure, but they can also contribute to further weight gain and inflammation, making it harder to lose weight in the long run.
The Role of Diet in Managing Inflammation and Supporting Weight Loss
- Anti-Inflammatory Foods:
- Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into your diet can help mitigate the effects of chronic inflammation. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids (such as fatty fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds), fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and spices like turmeric can reduce inflammation and support weight loss efforts.
- Balanced Nutritional Approach:
- A balanced diet that emphasizes nutrient-dense foods can help manage inflammation and support healthy weight loss. Avoiding processed foods, excessive sugar, and trans fats is crucial for minimizing inflammation and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Hydration and Lifestyle Factors:
- Staying hydrated and adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular physical activity, stress management, and adequate sleep can further help reduce inflammation and support weight loss goals.
Inflammation’s Impact on Appetite and Cravings
Inflammation is a complex biological response that can significantly influence appetite regulation and food cravings. While a normal inflammatory response is essential for healing and defense against infection, chronic inflammation can lead to various physiological changes that disrupt the body’s ability to maintain a healthy appetite and make balanced food choices. Understanding how inflammation affects appetite and cravings can help individuals make informed decisions about their dietary habits, especially when trying to manage weight or improve overall health.
How Inflammation Alters Appetite Regulation
- Disruption of Hormonal Signals:
- Inflammation can interfere with the balance of hormones that regulate appetite, primarily leptin and ghrelin. Leptin is produced by fat cells and signals to the brain when the body has enough energy stored, promoting feelings of fullness. Chronic inflammation can lead to leptin resistance, meaning the brain does not receive the “full” signal effectively, resulting in increased hunger and overeating. Conversely, ghrelin, often called the “hunger hormone,” may be elevated during periods of inflammation, stimulating appetite and cravings for high-calorie foods.
- Effects on the Hypothalamus:
- The hypothalamus is the brain region responsible for regulating hunger and satiety. Inflammatory cytokines, which are signaling molecules produced during inflammation, can impact the functioning of the hypothalamus. Elevated levels of these cytokines may alter the brain’s signaling pathways, leading to increased appetite and food intake, particularly of energy-dense foods that are often high in sugar and unhealthy fats.
Cravings for Specific Foods
- Increased Cravings for Comfort Foods:
- Chronic inflammation often leads to cravings for high-sugar and high-fat comfort foods. These foods can provide temporary relief and emotional comfort, but they may further exacerbate inflammation, creating a vicious cycle. The desire for these foods may stem from the brain’s reward system, which becomes activated by the consumption of sugary or fatty foods, providing a sense of pleasure and reinforcing the craving.
- Impact on Food Choices:
- When individuals are experiencing inflammation, their food choices may lean towards less nutritious options. The drive to satisfy cravings can lead to the consumption of processed foods, fast food, and sugary snacks, which can contribute to further inflammation and weight gain. This cycle can make it increasingly challenging to maintain a balanced diet and achieve weight management goals.
The Role of Stress and Psychological Factors
- Stress-Induced Inflammation:
- Stress is a significant contributor to inflammation, and it can also impact appetite and cravings. When under stress, individuals may seek out comfort foods to cope, leading to emotional eating and further inflammation. This response can create a cycle of stress, inflammation, and unhealthy eating habits.
- Psychological Connection:
- The psychological aspects of inflammation and appetite should not be overlooked. Chronic inflammation can lead to feelings of fatigue, depression, and anxiety, which may further drive individuals to seek comfort in food. Understanding the emotional components of eating can help individuals develop healthier coping strategies.
Chronic Inflammation and Hormonal Balance
Chronic inflammation is increasingly recognized as a significant factor affecting hormonal balance and overall health. Unlike acute inflammation, which is a necessary response to injury or infection, chronic inflammation persists over time and can lead to various health issues, including hormonal imbalances. Understanding the relationship between chronic inflammation and hormonal balance is crucial for those seeking to maintain optimal health and well-being.
How Chronic Inflammation Disrupts Hormonal Balance
- Impact on Insulin Sensitivity:
- Chronic inflammation can lead to insulin resistance, a condition where the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin. This hormone is crucial for regulating blood sugar levels and fat storage. When insulin sensitivity declines, the body compensates by producing more insulin, which can lead to higher levels of circulating insulin (hyperinsulinemia). This imbalance not only increases the risk of type 2 diabetes but can also promote weight gain and increase fat storage, particularly in the abdominal area.
- Influence on Leptin and Ghrelin:
- Leptin and ghrelin are hormones that play pivotal roles in appetite regulation. Leptin, produced by adipose (fat) tissue, signals fullness to the brain, while ghrelin, produced in the stomach, stimulates hunger. Chronic inflammation can lead to leptin resistance, meaning the brain does not receive adequate signals of satiety, resulting in increased appetite and potential overeating. Concurrently, ghrelin levels may be elevated during periods of inflammation, further driving hunger and cravings for high-calorie foods.
- Effects on Cortisol Levels:
- Cortisol, known as the stress hormone, is produced by the adrenal glands in response to stress. Chronic inflammation can lead to dysregulation of cortisol production, resulting in elevated levels of this hormone. Prolonged high cortisol levels can contribute to weight gain, especially in the abdominal region, disrupt sleep patterns, and affect overall mood and energy levels. Furthermore, chronic stress and inflammation can create a feedback loop, where high cortisol levels perpetuate inflammation.
Hormonal Effects on Reproductive Health
- Imbalance in Sex Hormones:
- Chronic inflammation can disrupt the balance of sex hormones, including estrogen and testosterone. In women, elevated inflammation levels are associated with menstrual irregularities and conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which is characterized by insulin resistance and hormonal imbalances. In men, chronic inflammation can lead to lower testosterone levels, affecting libido, energy levels, and overall well-being.
- Thyroid Function:
- The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism, energy levels, and growth. Chronic inflammation can impair thyroid function, leading to hypothyroidism or other thyroid-related disorders. This can result in symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and difficulty concentrating.
Managing Chronic Inflammation for Hormonal Balance
- Adopting an Anti-Inflammatory Diet:
- Eating a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help mitigate the effects of chronic inflammation on hormonal balance. Incorporating fruits, vegetables, whole grains, healthy fats (like omega-3 fatty acids), and lean proteins can reduce inflammation and support hormonal health.
- Regular Physical Activity:
- Engaging in regular exercise has been shown to reduce inflammation and improve insulin sensitivity. Physical activity can also help regulate cortisol levels, promoting overall hormonal balance and enhancing well-being.
- Stress Management Techniques:
- Implementing stress-reduction techniques, such as mindfulness, yoga, and meditation, can help lower inflammation levels and improve hormonal balance. Managing stress effectively is key to breaking the cycle of chronic inflammation and its impact on hormone regulation.
Dietary Choices and Inflammation
Diet plays a crucial role in influencing inflammation in the body. While certain foods can trigger or exacerbate inflammation, others can help mitigate its effects and promote overall health. Understanding the connection between dietary choices and inflammation is essential for anyone looking to improve their health, manage chronic conditions, or maintain a healthy weight.
Foods That Promote Inflammation
- Processed Foods:
- Highly processed foods, including fast food, snacks, and sugary beverages, often contain unhealthy fats, sugars, and preservatives that can trigger inflammatory responses. These foods can lead to weight gain and increase the risk of chronic diseases associated with inflammation.
- Sugar and Refined Carbohydrates:
- Excessive consumption of sugar and refined carbohydrates, such as white bread, pastries, and sugary cereals, can spike blood sugar levels and lead to insulin resistance. This condition can promote inflammation and contribute to various health issues, including obesity and metabolic syndrome.
- Trans Fats:
- Trans fats, commonly found in fried foods, margarine, and many processed snacks, are known to increase levels of inflammatory markers in the body. These unhealthy fats can also lead to cardiovascular problems and exacerbate chronic inflammation.
- Omega-6 Fatty Acids:
- While omega-6 fatty acids are essential for health, an overabundance in the diet, often from vegetable oils (like corn, soybean, and sunflower oils), can promote inflammation when not balanced with omega-3 fatty acids.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods
- Fruits and Vegetables:
- A diet rich in colorful fruits and vegetables provides a wealth of antioxidants and phytochemicals that can help reduce inflammation. Foods like berries, leafy greens, broccoli, and tomatoes are particularly beneficial due to their high nutrient density and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Healthy Fats:
- Incorporating sources of healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, can help combat inflammation. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish (like salmon, mackerel, and sardines) are especially potent in reducing inflammatory responses in the body.
- Whole Grains:
- Whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole oats, provide fiber and essential nutrients that can help lower inflammation levels. The fiber in whole grains supports gut health, which is linked to reduced inflammation.
- Herbs and Spices:
- Many herbs and spices, such as turmeric, ginger, and garlic, have been shown to possess anti-inflammatory properties. Turmeric, in particular, contains curcumin, a powerful compound known for its ability to inhibit inflammatory pathways in the body.
The Role of Hydration
- Water and Inflammation:
- Staying well-hydrated is vital for overall health and can help manage inflammation. Dehydration can lead to increased levels of inflammatory markers. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day, as well as incorporating herbal teas and other low-sugar beverages, can support hydration and help mitigate inflammation.
Lifestyle Factors Beyond Diet
- Physical Activity:
- Regular physical activity can also play a significant role in reducing inflammation. Exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, improves insulin sensitivity, and can directly lower inflammatory markers in the body.
- Stress Management:
- Chronic stress can contribute to inflammation. Implementing stress-reduction techniques, such as mindfulness, yoga, and adequate sleep, can complement dietary changes and enhance overall well-being.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of inflammation and understanding when to seek medical advice is essential for maintaining overall health. Chronic inflammation can significantly impact the body, leading to various health issues, including weight loss, hormonal imbalances, and chronic diseases. Here are some key indicators that it may be time to consult a healthcare professional regarding inflammation and its potential effects on weight loss:
1. Unexplained Weight Loss
- Description: If you experience significant, unintentional weight loss (typically defined as losing 5% or more of your body weight in six months without trying), it could be a sign of an underlying health issue. Chronic inflammation can contribute to weight loss by affecting appetite, metabolism, and nutrient absorption.
- When to Seek Help: Consult your healthcare provider if you notice unexplained weight loss alongside other symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, or changes in appetite. This can help identify potential underlying causes, including inflammatory conditions.
2. Persistent Fatigue and Low Energy
- Description: Chronic inflammation often leads to fatigue and low energy levels. If you find yourself feeling excessively tired despite adequate rest, it may be a sign that your body is fighting ongoing inflammation.
- When to Seek Help: If fatigue persists for weeks and significantly impacts your daily activities, it’s important to discuss your symptoms with a healthcare professional. They can evaluate for potential causes, including inflammatory disorders or other health conditions.
3. Joint Pain and Swelling
- Description: Inflammation can lead to pain, swelling, and stiffness in the joints. Conditions such as arthritis or other inflammatory diseases can manifest as joint discomfort and may affect your ability to exercise or maintain a healthy lifestyle.
- When to Seek Help: If you experience persistent joint pain, swelling, or limited range of motion, consult a healthcare provider for evaluation and potential treatment options. Early intervention can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
4. Digestive Issues
- Description: Chronic inflammation can disrupt gut health, leading to symptoms like bloating, diarrhea, constipation, or unexplained gastrointestinal discomfort. Conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) or food sensitivities can contribute to these symptoms.
- When to Seek Help: If you frequently experience digestive issues that do not improve with dietary changes or over-the-counter remedies, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management.
5. Skin Changes
- Description: Inflammation can also manifest through skin conditions such as rashes, redness, or swelling. Conditions like eczema, psoriasis, or chronic hives can be linked to underlying inflammatory processes.
- When to Seek Help: If you notice persistent or worsening skin changes, seek advice from a dermatologist or healthcare provider. They can assess your symptoms and recommend appropriate treatment options.
6. Symptoms of Chronic Illness
- Description: If you experience symptoms commonly associated with chronic illnesses, such as fever, night sweats, or unexplained changes in your health status, it may indicate ongoing inflammation or a more serious underlying condition.
- When to Seek Help: Consult your healthcare provider if you have any concerning symptoms that persist over time or worsen. Early diagnosis and intervention can be crucial for managing chronic conditions effectively.
Conclusion
Chronic inflammation is a critical factor that can significantly hinder your weight loss journey and overall health. By understanding the complex relationship between inflammation and weight management, individuals can take proactive steps to address this underlying issue. Chronic inflammation can disrupt hormonal balance, impact metabolism, and alter appetite regulation, making it more challenging to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
Recognizing the role of dietary choices, physical activity, and stress management in reducing inflammation is essential for anyone seeking to shed pounds. Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet rich in whole foods, healthy fats, and lean proteins can not only support weight loss efforts but also improve overall well-being. Additionally, incorporating regular exercise and effective stress management techniques can further help mitigate inflammation and its effects on the body.
Ultimately, addressing chronic inflammation requires a holistic approach that considers lifestyle, nutrition, and mental health. By prioritizing strategies that combat inflammation, you can enhance your ability to lose weight effectively and sustainably. If you find yourself struggling with unexplained weight changes or other symptoms of chronic inflammation, seeking guidance from healthcare professionals can provide valuable support and ensure a comprehensive plan tailored to your individual needs. Embracing this proactive approach can lead to lasting health improvements and a more fulfilling weight loss journey.
FAQs
1. What is chronic inflammation, and how does it affect weight loss?
Chronic inflammation is a prolonged inflammatory response that can persist for months or years, often due to factors like poor diet, stress, or underlying health conditions. It can disrupt hormonal balance, increase insulin resistance, and alter appetite regulation, making it more difficult to lose weight.
2. What foods should I avoid to reduce inflammation?
To reduce inflammation, it’s best to limit or avoid processed foods, refined sugars, trans fats, and excessive omega-6 fatty acids. Instead, focus on reducing or eliminating foods high in sugar, unhealthy fats, and refined carbohydrates.
3. What anti-inflammatory foods can help with weight loss?
Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods can support weight loss and overall health. Some excellent options include:
- Fatty fish (like salmon and mackerel)
- Fruits (especially berries)
- Vegetables (especially leafy greens)
- Nuts and seeds
- Whole grains (like quinoa and brown rice)
- Healthy fats (like olive oil and avocados)
4. Can exercise help reduce inflammation and support weight loss?
Yes, regular physical activity has been shown to reduce inflammation and improve insulin sensitivity. Engaging in moderate aerobic exercise and strength training can help mitigate the effects of chronic inflammation and enhance weight loss efforts.
5. How does stress contribute to chronic inflammation and weight gain?
Chronic stress can lead to elevated levels of cortisol, a hormone that, when in excess, can promote fat storage, especially in the abdominal area. It can also trigger unhealthy eating habits, leading to weight gain and exacerbating inflammation.
6. Are there specific symptoms of chronic inflammation I should be aware of?
Common symptoms of chronic inflammation include fatigue, joint pain, digestive issues, skin problems, and unexplained weight changes. If you experience any of these symptoms persistently, it may be time to consult a healthcare professional.
7. How can I effectively manage chronic inflammation?
Managing chronic inflammation typically involves a combination of dietary changes, regular physical activity, stress management techniques, and getting adequate sleep. Adopting an anti-inflammatory lifestyle can help reduce inflammation levels and improve overall health.
8. When should I seek medical advice regarding inflammation and weight loss?
If you experience unexplained weight loss, persistent fatigue, joint pain, digestive issues, skin changes, or symptoms of chronic illness, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for evaluation and potential treatment options.
9. Is there a connection between inflammation and metabolic disorders?
Yes, chronic inflammation is linked to various metabolic disorders, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. Inflammation can disrupt metabolic processes and contribute to insulin resistance, complicating weight loss efforts.
10. Can weight loss itself reduce chronic inflammation?
Yes, losing excess weight can significantly reduce inflammation levels in the body. Adopting a healthy lifestyle that promotes weight loss can lead to decreased inflammatory markers and improved overall health.



Do you mind if I quote a few of your posts as long as I provide credit and sources back to your site? My blog is in the exact same niche as yours and my visitors would really benefit from some of the information you present here. Please let me know if this alright with you. Thanks!